An essential for advanced semiconductors — A look at MANAC’s “TIP” as a next-gen resist raw material
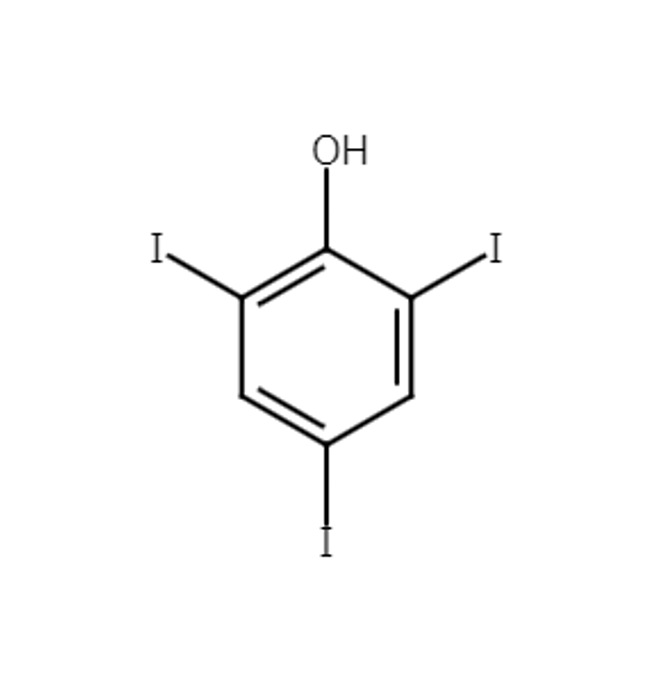
【CAS No.】609-23-4
【Chemical name】2,4,6-Triiodophenol
【Chemical formula】C6H3I3O
The semiconductor industry has shown spectacular growth and development in recent years, as evidenced by the February 2024 operational launch of the new Kumamoto Factory established by TSMC, a company that commands the world’s largest share of semiconductor foundries. Semiconductors comprise the “heart” that drives the inner workings of cellphones, computers, and other digital electronics, and are also essential to cutting-edge technologies, including generative AI and electric vehicles (EV).
With the demand for semiconductors soaring, the importance of supply chains for the required manufacturing materials is also rising from an economic security standpoint.
Amid such developments, the iodine compound manufactured by MANAC known as “TIP” has been gaining attention both in and outside Japan. TIP is largely considered essential for producing the most cutting-edge semiconductors, so we invite you to join us in taking a quick look at this compound.
contents
Endless possibilities through simplicity — A look at the “TIP” iodine compound
The commonly used term “TIP” stands for 2,4,6-triiodophenol. TIP is a compound comprised of three iodine atoms bonded to phenol, making its structure incredibly simple.
Simple molecules like TIP are used as “parts” to create large or complex molecules. In other words, coupling TIP with other molecules allows for the creation of a wide range of compounds. Currently, the TIP compound is used in this capacity in many fields, including pharmaceuticals and electronic materials.
In recent years, TIP has also garnered attention as a raw material for “resists” used in semiconductor manufacturing.
The resist materials indispensable to drawing circuits onto semiconductors
Semiconductors are fabricated by forming extremely tiny circuits onto thin slices of silicon, commonly called wafers. The functions of resist, a photosensitive material, are paramount to this process.
Semiconductor circuits are often formed through the following general process.
(1) Deposition: A thin film (the etching film) is formed on the silicon wafer to serve as the circuit substrate layer.
(2) Resist coating: A resist material is applied on top of the etching film to form a resist film.
(3) Photolithography: Light is applied to the resist film through a plate (called a photomask) printed with the targeted circuit pattern. The portions of the resist material exposed to the light undergo property changes, increasing either the solubility or the insolubility compared to areas not exposed to light.
(4) Development: Development solution is applied to the resist film. In this step, the portions of the resist material exposed to light in Step (3) are selectively dissolved or selectively protected from dissolving, leaving behind the circuit pattern left by the photomask.
(5) Etching: Portions of the etching film not protected by the resist material are removed.
(6) Resist removal: Any material remaining from the resist layer is removed, leaving the pattern from the photomask transferred onto the etching film.
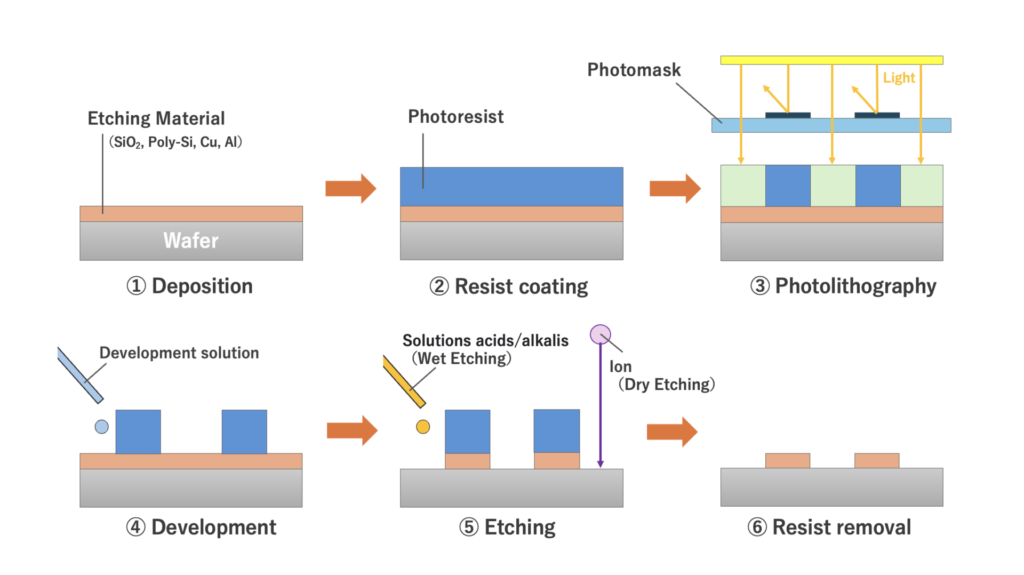
The resist material plays a crucial role as a “mediator” in transferring the circuit pattern printed on the photomask into the etching material. Semiconductor fabrication is simply not possible without resist materials.
TIP is a raw material used to make resist materials. TIP enjoys broader applicability over other iodine compounds owing to its incredibly simple structure. Using TIP molecules as “parts” enables extensive utility in researching and developing resist materials for customers, assisting in synthesizing resist materials with complex structures.
Shrinking semiconductors with the power of TIP
In a world full of resist materials of various structures, resist materials that utilize TIP offer a major advantage. That advantage is none other than the ability to manufacture cutting-edge semiconductors with extraordinarily tiny circuits.
In fact, semiconductor circuits are shrinking by the year. Making circuits smaller brings many benefits, including decreased power consumption and higher performance.
An aspect essential to achieving smaller circuits is the wavelength of the light used during the photolithography exposure process. In general, the shorter the wavelength of the light, the smaller the size of the circuit pattern that can be drawn into the resist material. In practical terms, this means that the light employed during the photolithography exposure process must have a wavelength shorter than the target circuit lines to be formed. It also signifies that further advancements in decreased semiconductor transistor size require resist materials that react to light of even shorter wavelengths.
Here to help realize such advancements are resist materials made with TIP. Since TIP and other resist materials that contain iodine compounds react to the amazingly short light wavelength of 13.5 nm, they are perfect for fabricating highly sought-after cutting-edge semiconductors.
Resist materials made using TIP occupy a role as a material that is clearly essential for further advancements in the semiconductor industry.
High-quality, low-cost TIP made possible by MANAC’s technologies
The development of low-cost, high-purity TIP is a notable achievement among MANAC’s work to develop iodine compounds. MANAC has started its provision of TIP to a wide range of fields, including the semiconductor industry.
One of our strengths at MANAC is the ability to provide a stable supply of iodine, a raw material of TIP. Even with the ongoing global shortage of iodine supplies, MANAC maintains facilities and processes that enable the continuous manufacturing of low-cost, high-purity TIP.
Demand for TIP is expected to keep rising as further semiconductor advancements are achieved. Likewise, MANAC will continue to strive in its endeavor to provide reliability and high quality through the manufacturing and marketing of TIP.