Recommending DBDMH over the requested brominating agent and contributing toward reduced manufacturing costs for clients
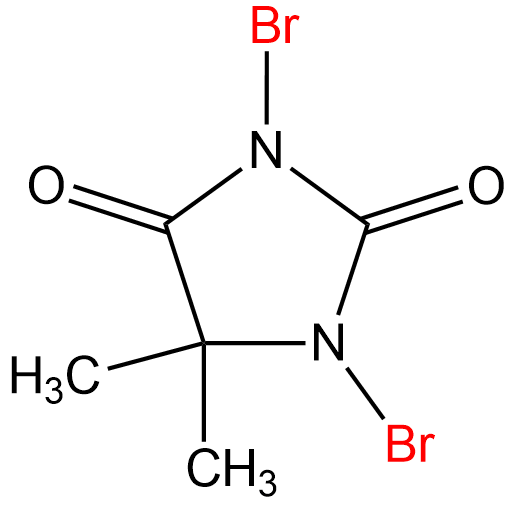
【CAS No.】77-48-5
【Chemical name】1,3-Dibromo-5,5-dimethylhydantoin
【Chemical formula】C5H6Br2N2O2
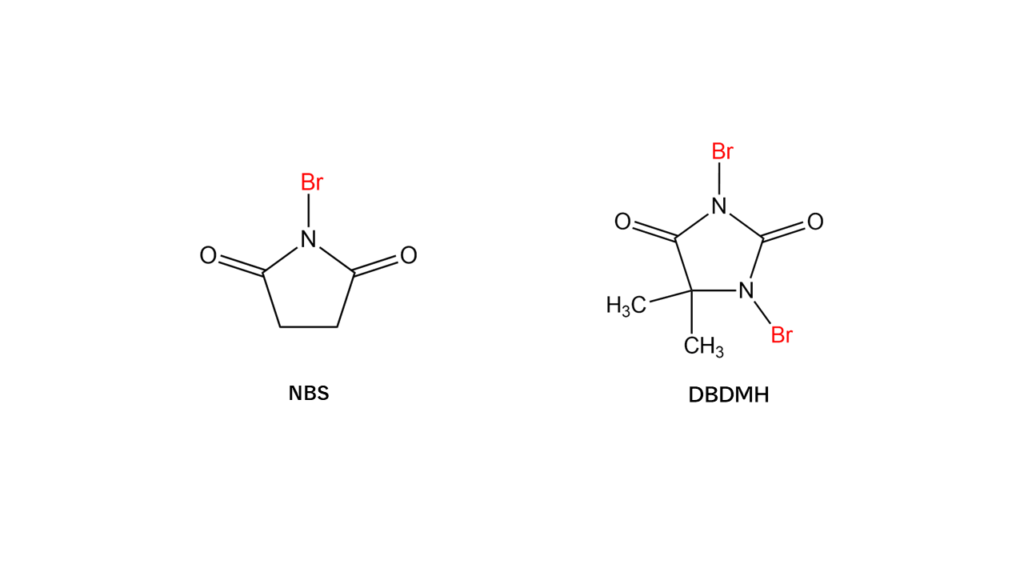
In addition to halogen compounds that contain halogens such as bromine and iodine, Manac also manufactures and markets the brominating agents required to produce halogen compounds. Examples of the brominating agents handled by Manac include NBS and DBDMH.
In winter 2019, Go Tanaka, in charge of pharmaceutical-related product sales at Manac’s sales department, received an order for NBS from a company. Mr. Tanaka was able to lower manufacturing costs for the client by recommending DBDMH as an alternative brominating agent.
What led Mr. Tanaka to recommend this alternative agent? This article covers the story while reviewing the differences between NBS and DBDMH.
■ What you can learn from this article ✔ Mr. Go Tanaka proposed DBDMH as an alternative to NBS, successfully reducing the client’s manufacturing costs. ✔ DBDMH can achieve bromination with less quantity than NBS, making it cost-effective. ✔ Manac prioritizes making optimal recommendations based on the client’s development stage. ■ Recommended Articles ・ Bromoallene synthesis from propargv alcohol, ortho-selective bromination of aromatic rings: NBS bromination reactions (5): N-bromo compounds (7): Discussion series on bromination/iodination reactions 7 ・ A fascinating brominating agent capable of minimizing costs and byproducts, describing 1,3-dibromo-5,5-dimethylhydantoin (DBDMH): N-bromo compounds (8): Discussion series on bromination/iodination reactions 8 ・ MANAC’s three strengths in manufacturing active pharmaceutical ingredients and intermediates ・ Bromination reactions with hydrogen bromide (additions to alkenes/alkynes): Hydrogen bromide (3): Discussion series on bromination/iodination reactions 36
contents
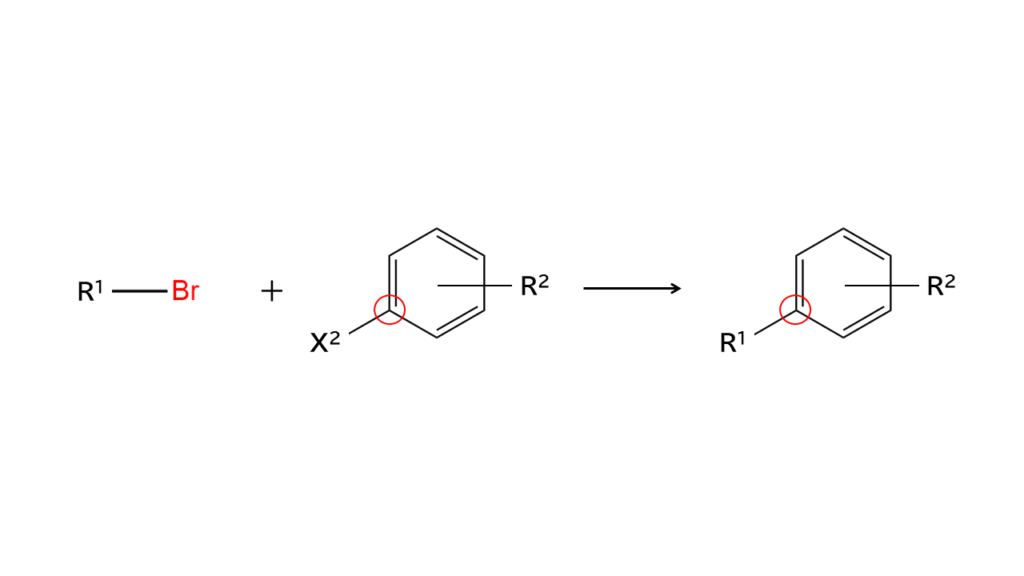
What are brominating agents?
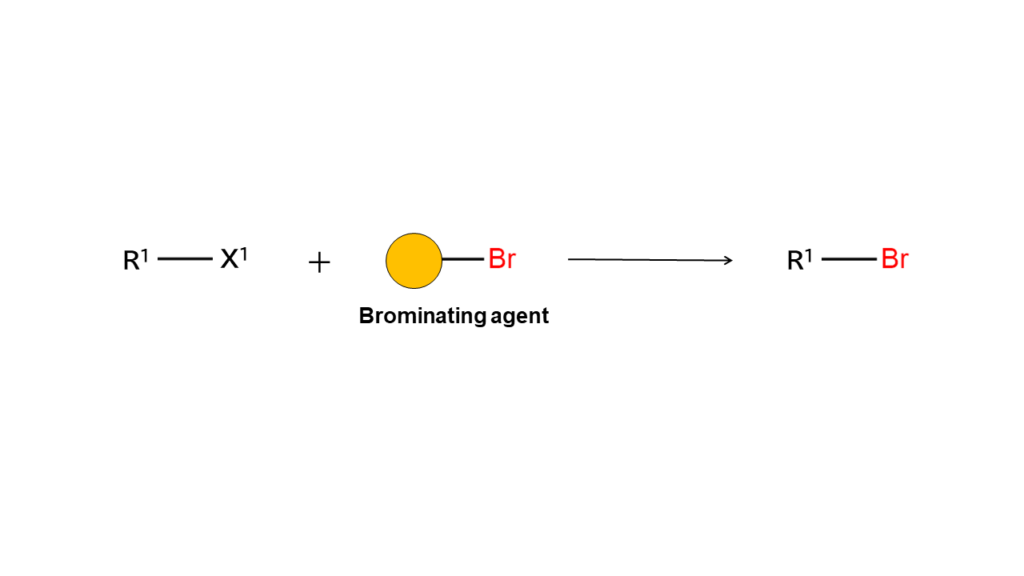
Brominating agents are reagents used to make bromo compounds (compounds containing bromine) by bonding bromine (Br) to compounds. By mixing a brominating agent with a target compound and setting the appropriate temperature, the bromine in the brominating agent will transfer to the target compound and form a bromo compound.
The bromine in bromo compounds acts as a “glue” to stick other compounds to its site. Many different chemical intermediates can be produced by “gluing” bromo compounds to a wide variety of other compounds.
Brominating agents are used to make intermediates in many fields, including for pharmaceutical products and electronic materials.
What kind of brominating agents are NBS and DBDMH?
Both NBS and DBDMH have structures in which nitrogen (N) atoms sit adjacent to a carbonyl group (C=O) and are bonded with bromine. Since these nitrogen atoms are highly reactive, the bromine atoms bonded to these nitrogen atoms break away easily. This makes it possible to transfer bromine atoms to other compounds.
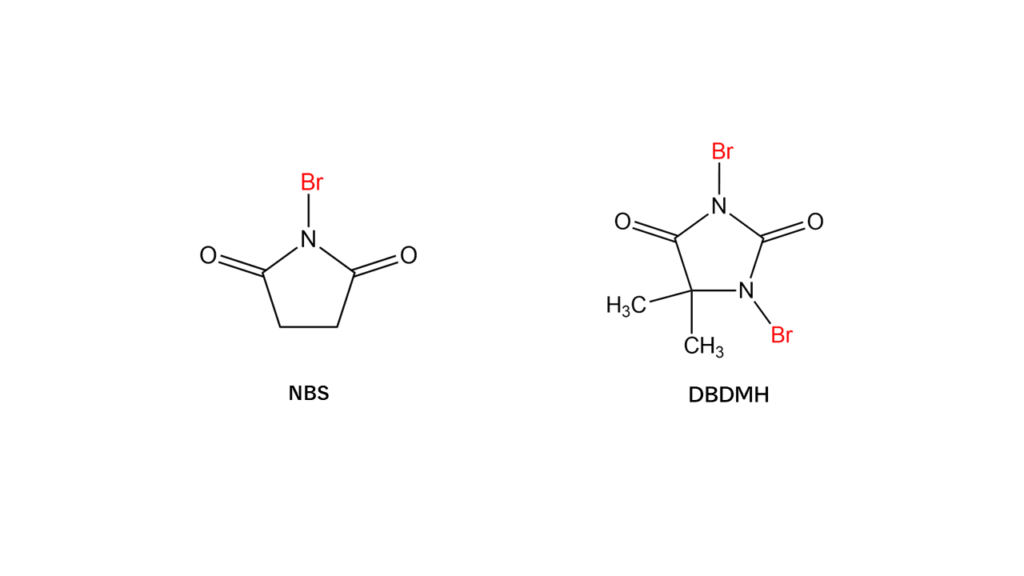
The number of bromine atoms differs between NBS and DBDM compounds, with one bromine atom in NBS and two in DBDMH.
When using NBS to produce bromo compound A, it is necessary to use the same amount of NBS as the original compound being targeted for bromination. In the case of DBDMH, one DBDMH compound can brominate two target compounds since DBDMH contains two bromine atoms. This means that DBDMH can be used to produce bromo compound A using half the amount required with NBS.
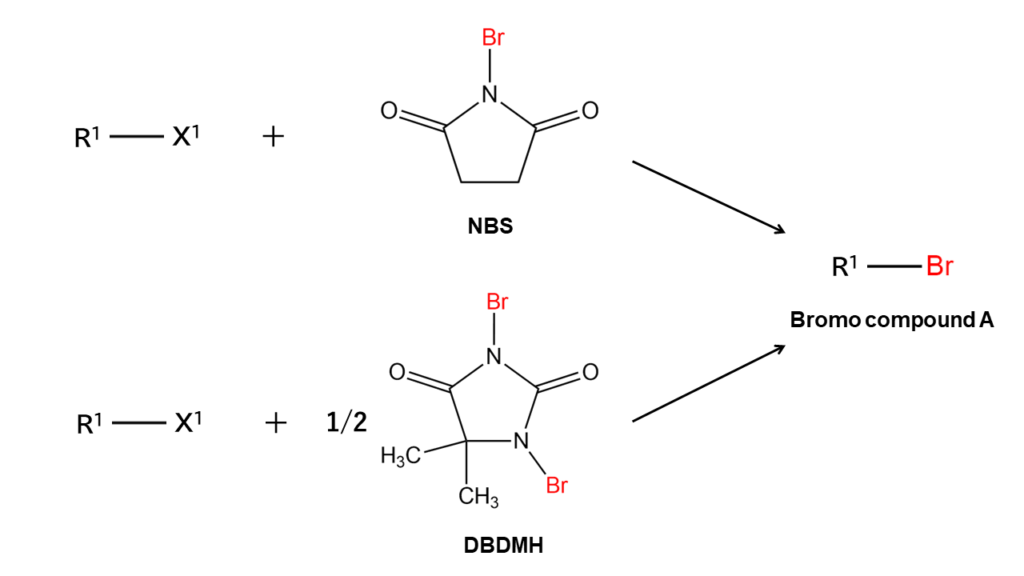
Although DBDMH can achieve bromination more efficiently than NBS, companies in the chemicals industry generally use NBS, and not many companies handle DBDMH, including those in Japan. DBDMH is not widely known, which is why the company requested NBS when they first contacted Manac.

Why Manac recommended DBDMH as an alternative to NBS
Manac handles both NBS and DBDMH. However, as explained above, since bromination can be achieved using less DBDMH than NBS, there is potential for DBDMH to lower manufacturing costs compared to NBS for the client. In addition, NBS and DBDMH have an equal level of reactivity, and post-processing can be handled in the same way. These factors led Manac to recommend DBDMH as an alternative to NBS.
In this case, the client was fortunately in a relatively early stage of its development. If the development had been at a somewhat more advanced stage, changing the brominating agent from NBS to DBDMH would have required additional work, such as retaking experimental data and producing manufacturing procedural documentation. However, in this case, the client had only just made a prototype using NBS, so the brominating agent could be switched to DBDMH without causing any major issues.
Offering suitable alternative recommendations in consideration of the client’s costs, method of use, and stage of development, that is the comprehensive approach to sales at Manac.
Considering manufacturing processes together with clients
Manac not only recommends brominating agents, it also offers recommendations for optimal manufacturing processes. When a client approaches Manac with a specific compound they want to make, Manac works closely with the client to develop manufacturing processes with even higher efficiency. The great amount of data and expertise amassed by Manac through their vast experience with various syntheses allows them to take this kind of client-centric approach to the development of manufacturing processes.