Making complex compounds a breeze! The heterohalogen series
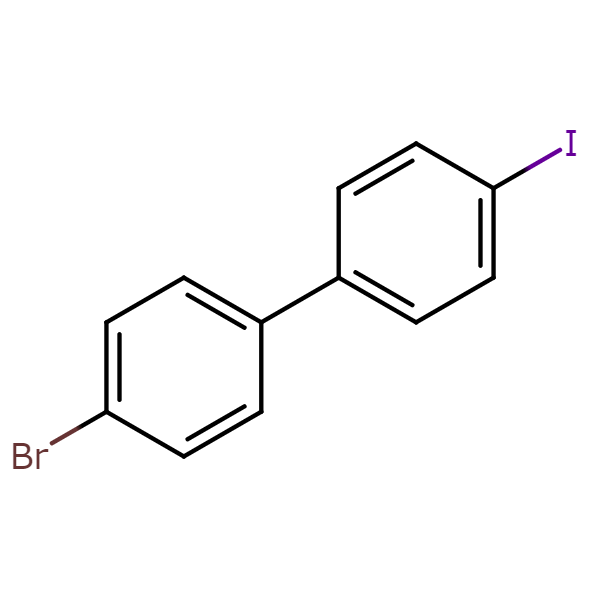
【CAS No.】105946-82-5
【Chemical name】4-Bromo-4′-iodobiphenyl
【Chemical formula】C12H8BrI
Manac produces and markets compounds that contain halogen elements (halogen compounds), such as bromine and iodine, and are used as intermediate compounds in products such as medication, flavorants, electronic materials, and photoconductive materials. Examples of Manac’s product series include alkyl halides, alpha-bromo compounds, and heterohalogen compounds.
This article reviews the characteristics and applications of the heterohalogen compound series, which can be used when producing complex final compounds.
■ What you can learn from this article ✔ Manac specializes in producing heterohalogen compounds containing bromine and iodine. ✔ Heterohalogen compounds are used to control bonding and create complex final compounds. ✔ Manac can handle complete manufacturing, from intermediates to higher-order compounds. ■ Recommended Articles ・ Extensive use in electronic material intermediates and beyond! The alkyl halide series ・ The alpha-bromo compound series – Determining acidic or alkaline qualities ・ Hydrocarbon iodination: Aromatic compound iodination overview and reactions: Aromatic compound iodination reactions (1): Discussion series on bromination/iodination reactions 15
contents
What are heterohalogen compounds?
Heterohalogen compounds are compounds that contain two or more types of halogen elements. Manac is particularly specialized in heterohalogen compounds that contain bromine and iodine.
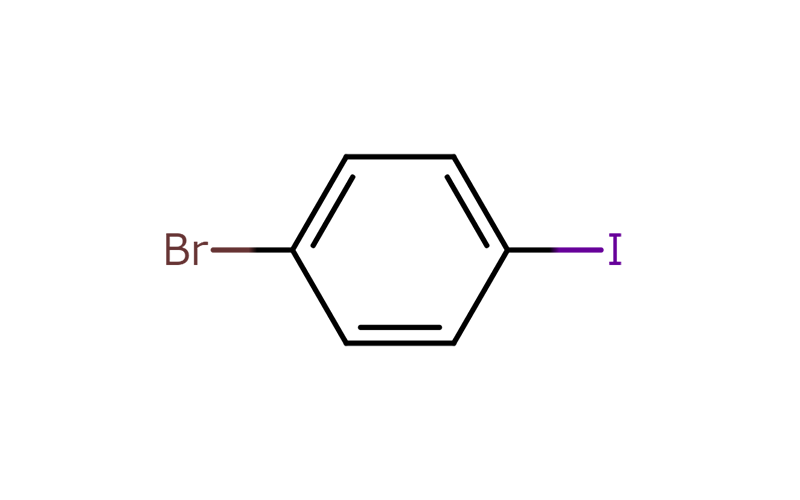
“Gluing” compounds together using halogen sites
Joining two types of compounds is a two-step process:
- Break the original bonds in the two compounds
- Create new bonds between the two compounds
Usually, a large amount of energy is required to break the original bonds of a compound, but because bonds between carbon and halogens are relatively weak, a well-placed application of a small amount of energy can break their bonds. This causes the halogen sites in the heterohalogen compound to bond with other compounds (coupling reaction), causing the halogen to break away.
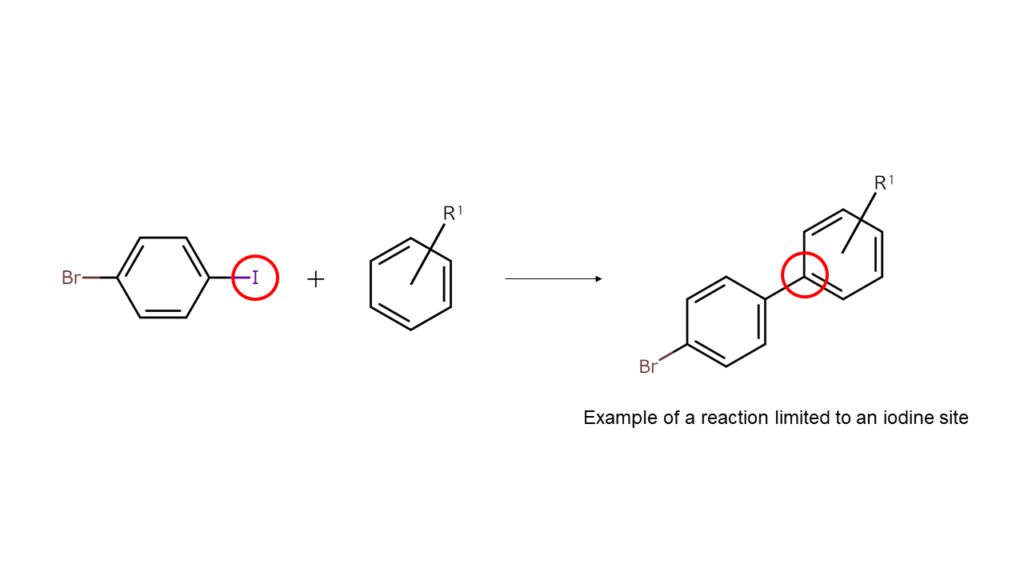
This means that the halogens that are present in heterohalogen compounds act as a “glue” to stick other compounds to its site.

Controlling the “gluing” order
The compounds (final compounds) used in electronic materials and medicines are generally of complex structures. In order to make final compounds, compound structures must be divided into several parts before joining the appropriate parts together. Heterohalogen compounds are ideal for use as one of these parts with their halogen sites acting as the glue.
As heterohalogen compounds contain two or more halogen elements, they are particularly capable of creating compounds of complex structures compared to Manac’s alkyl halide and alpha-bromo compound series. The following offers further explanation.
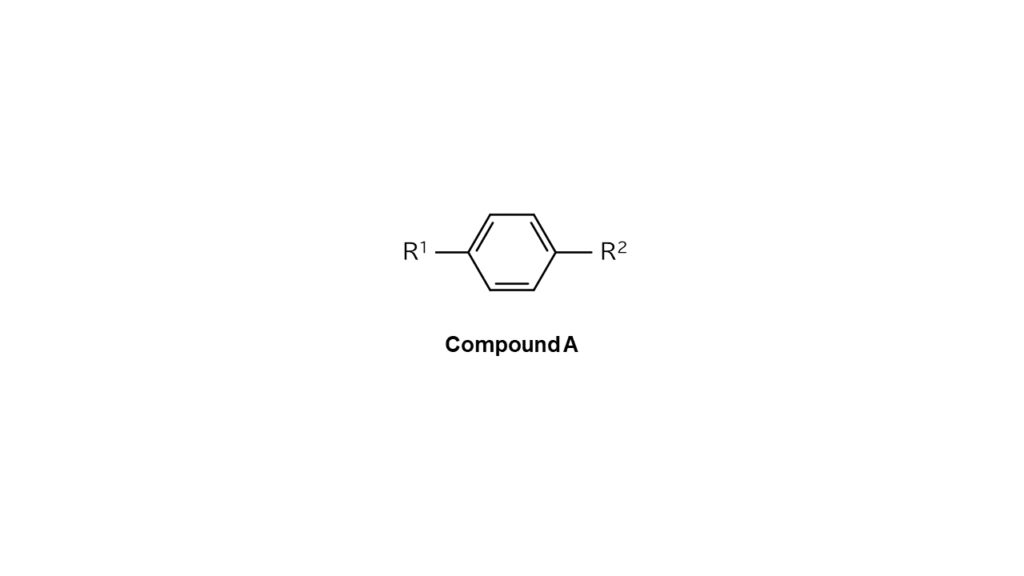
For example, let’s say we want to make compound A with R1 and R2, each with differing structures, bonded on a benzene ring’s reaction sides, as illustrated below.
We then use compound B, which only contains bromine as shown below, as the part to make compound A.
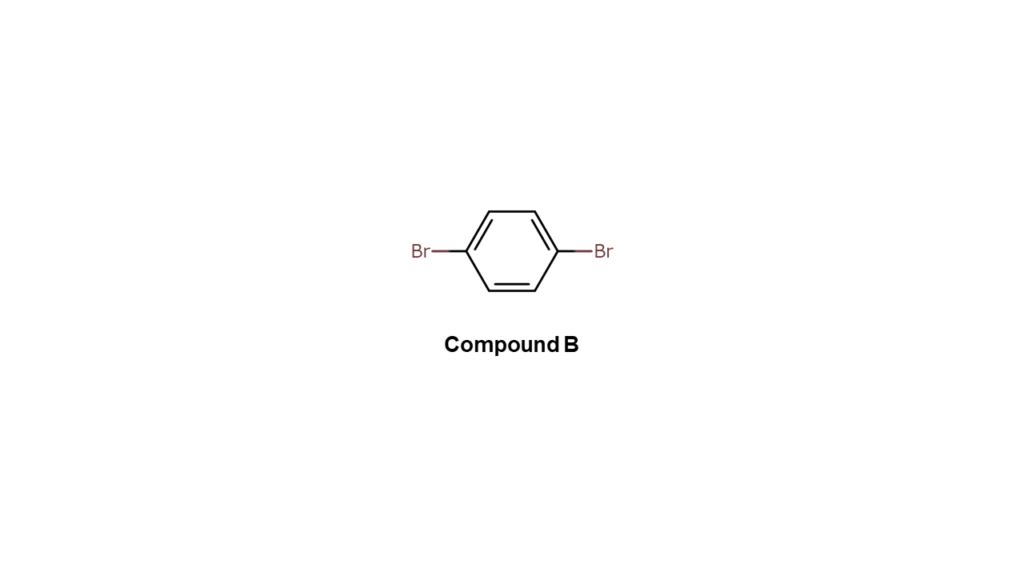
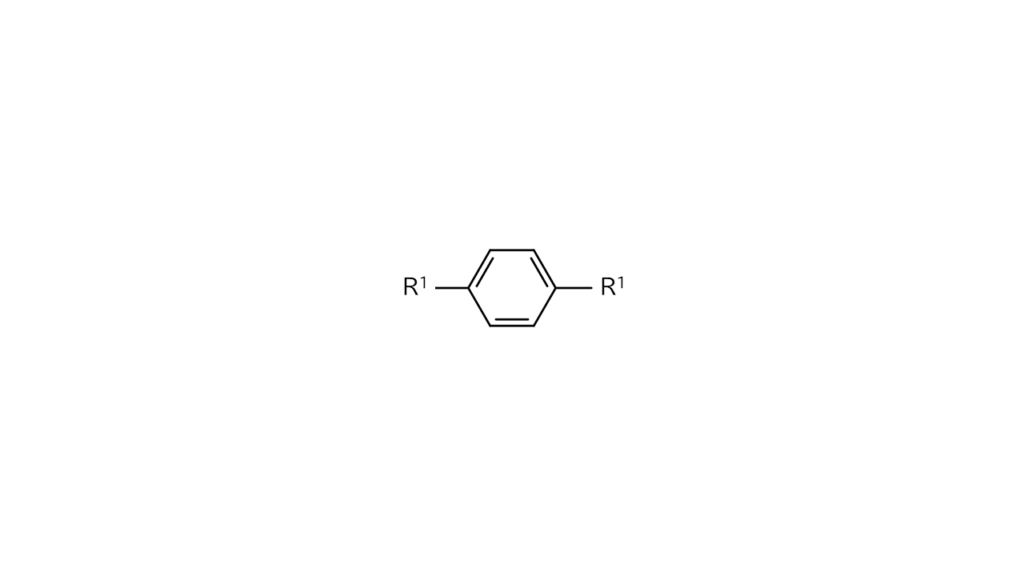
We wanted first to react compound B with the R1 site, bonding only the left bromine (Br) site of compound B with the R1 site. However, since compound B has identical bromine sites on both sides, bromine sites on the right side also ended up binding with R1 sites. Compound A cannot be produced with this approach.
Let’s then consider making compound A using compound C below, a heterohalogen compound containing bromine and iodine.
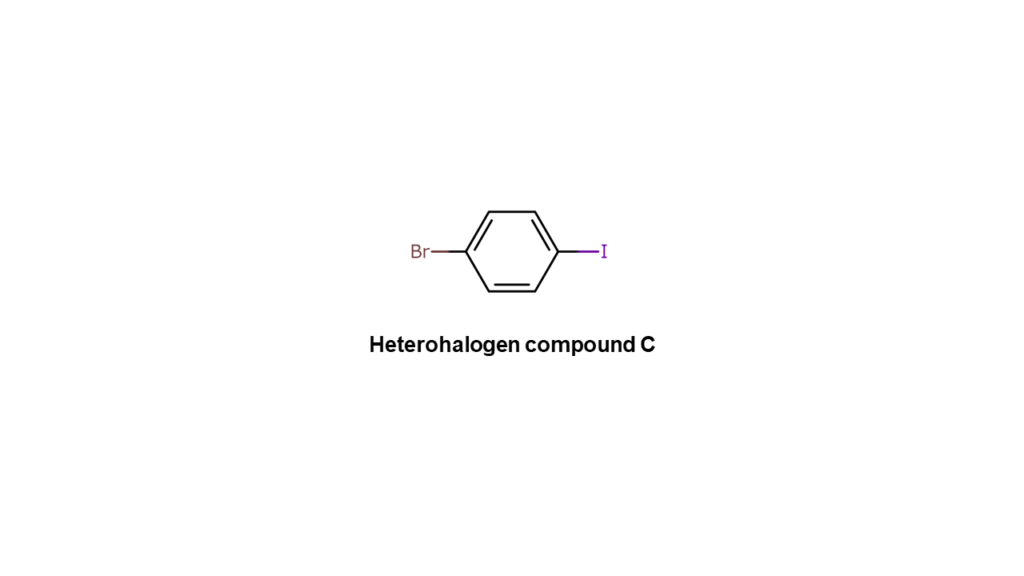
We first reacted heterohalogen compound C to the R1 site. Since carbon and iodine (I) bonds break more easily than carbon and bromine (Br) bonds, we obtained the compound below with only the R1 and iodine sites bonding.
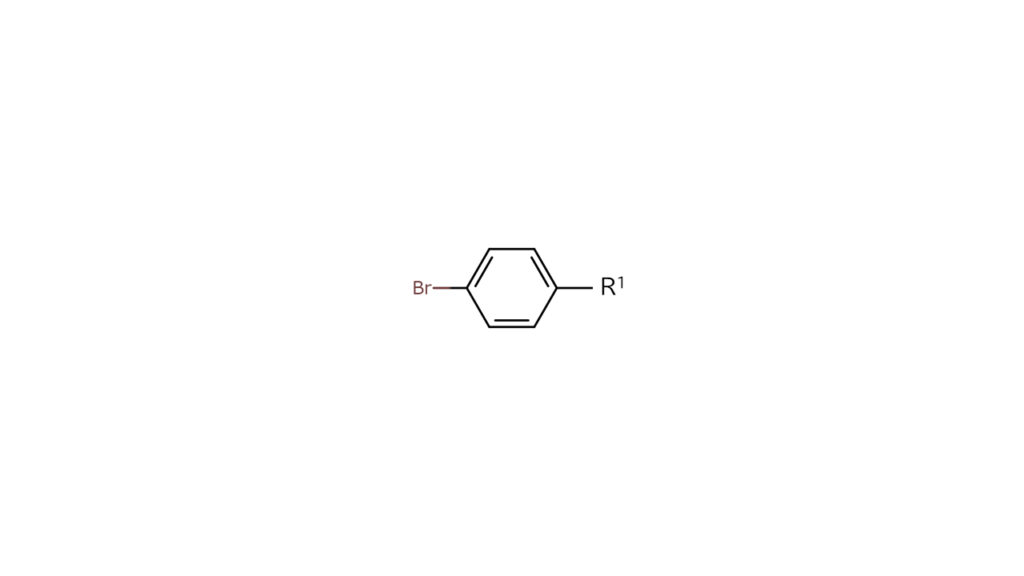
Next, we reacted the above compound with the R2 site. The R2 site bonds with the remaining bromine site, leaving us with the targeted compound A as shown below.

And that’s our general process. Basically, heterohalogen compounds are extremely useful when making complex compounds such as asymmetric final products like compound A above. This is a strength unique to heterohalogen compounds with their compositions of two or more halogens with differing reactivities.
Series list and applications of each heterohalogen compound
There are many different compounds in the heterohalogen compound series, which are mainly used as intermediates (parts) in products such as medicines and photoconductive materials. The following table lists the heterohalogen compounds marketed by Manac along with their applications and structural formulas. Be sure to check whether there are any “parts” in which you, the reader, may be interested.
Manac specializes not only in bromination and iodination to make heterohalogen compounds, but also in coupling reactions of various types using heterohalogen compounds. This enables Manac to handle complete orders, from manufacturing intermediates to producing higher-order compounds. If interested in any of the parts in the above catalog, please contact Manac for more details about higher-order compounds synthesized using those parts.